TAICHUNG,Taiwan, May 15, 2023 /PRNewswire/ -- After the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic, most people suffered from mild disease, and "Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)" is common for those critical COVID-19 patients. The 46-year-old of Ms. Chang, who had hypertension and nephropathy, accepted kidney transplantation surgery 10 years ago. She was tested positive for COVID-19 and had severe respiratory failure. Ms. Chang was diagnosed to have "Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)." At the negative pressure isolation ICU of China Medical University Hospital (CMUH), Ms. Chang immediately underwent endotracheal intubation, and ECMO emergent use was initiated to temporarily replace the lung function of Ms. Chang. Thanks to the visualized smart medicine system designed by CMUH to real-time monitor Ms. Chang's key respiratory therapy. Further, given proper antibiotics and antivirals to the patient, the condition of Ms. Chang was reversed and improved with 15 days of ECMO support. On the 23rd day, the endotracheal tube was removed, and Ms. Chang was getting stable and successfully recovered to be discharged after 35 days of hospitalization.
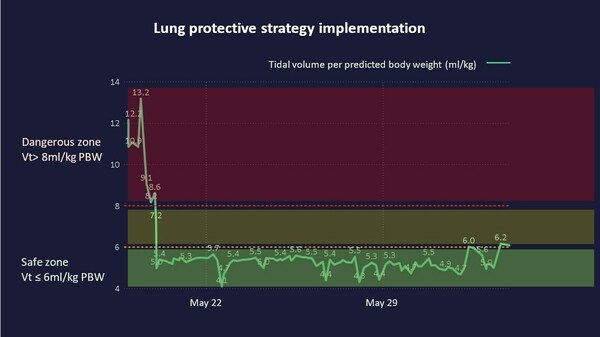
“CMUH Smart medicine system: ARDS real-time monitoring dashboard” ensured Ms. Chang’s “LPV,” the green zone meant the safety range of the lung volume during the acute phase for patient’s lung protection.
ARDS Needs Timely "LPV" Smart Medicine System Can Help Reduce the Mortality Rate of Critical Patients
Dr. Wei-Cheng Chen, V.S., Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, CMUH , stated that according to Ms. Chang's acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II score when first admitted to the isolated ICU, the predicted mortality rate was 70%; however, the medical care team accurately provided the Tidal Volume (TV) to protect the lungs from injury through the assistance of the smart medicine system. Furthermore, an interprofessional and cross-department "ARDS team" was gathered right away to save Ms. Chang with all their combined efforts, including physicians from pulmonary and critical care medicine, renal transplantation, infectious diseases, and cardiovascular surgery, nurse specialists, the respiratory technicians, technicians of extracorporeal technician, pharmacists, and nutritionists, who all teamed up to provide her with seamless care.
Dr. Wei-Cheng Chen explained that ARDS is a kind of diffuse pulmonary alveoli injury with fast progression that is accompanied with severe hypoxemia. It is a cross-specialty syndrome in critical care medicine, whose common causes may include all kinds of pneumonia, sepsis, lung contusion, pancreatitis, etc. Patients may be admitted to the ICU due to respiratory failure and multiple organ failure. Such conditions consume considerable medical manpower, resources, and interprofessional cooperation.
Dr. Wei-Cheng Chen further explained that ARDS is a pretty troublesome complication. As shown in the literature, the mortality rate of ARDS could be up to 80% in elderly and septic patients, even though respiratory treatment technology is significantly improved in modern medicine. Most ARDS patients need endotracheal intubation to survive and also need a timely diagnosis with a series of treatments to improve the prognosis. "Lung Protective Ventilation (LPV)" is currently the best treatment strategy with a strong evidence base."
Dr. Wei-Cheng Chen stated that the unsatisfactory implementation rate is raised by many domestic and international studies because the timing of the cross specialty care team intervention cannot be properly and accurately integrated. At China Medical University Hospital, the pulmonologists and critical care specialist have invited their colleagues to form the cross-specialty "ARDS team." In addition to nurse specialists, RT team, perfusionists, pharmacists, and nutritionists, the cardiovascular surgeon and physicians from emergency medicine were also invited; the most valuable part was inviting the information experts of the smart medicine system into the team as well. Through the Power business intelligence (BI) developed by Microsoft , the medical information and data of the ARDS patients were all visualized and integrated to be calculated by the system to provide real-time big data to support the medical team.
As a result, the medical team can provide individualized therapeutic strategies for ARDS patients based on the data. Under such a treatment model, most critical ARDS patients can successfully recover due to the conditions reversed by proper assessment and precise treatment implementation.
Outstanding Achievement of CMUH ARDS Team Published by Top International Medical Journal <Critical Care>
CMUH "ARDS team" applied the smart medicine system improved interface to help the cross-specialty team have a real-time visualized Dashboard to obtain universal control of the patient's medical data to cure the rapidly changing ARDS. Such excellent clinical care performance was highly recognized by the top international medical journal for emergency and critical care, "Critical care," and the related achievements were published in the journal in August 2022 with an article entitled "Using real–time visualization system for data driven decision support to achieve lung protective strategy: a retrospective observational study."
The outstanding achievement of CMUH's cross-specialty "ARDS team" on the critical care medicine was highly recognized by international emergency and critical care experts. The clinical research was published in an international journal with high Impact Factor of 19.3. Furthermore, Dr. Wei-Cheng Chen earned many domestic and international recognitions, including the best presenter and young investigator award at TSCCM/TSECCM/JSICM Joint Congress, TSECCM quality award, cross territory holistic health care best oral presentation award, first place of Taiwan Al Academy industrialization innovation competition, educational innovation award, and more.
Dr. Chieh-Lung Chen, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, CMUH, mentioned that, based on the APACHE II score, the level of critical conditions of ICU patients can be reflected, with a score over 20 belonging to the high risk group. After assessment, Ms. Chang had a score of 30 with a predicted mortality rate of 70%. Under the aggressive care of the ARDS team, Ms. Chang was given antibiotics and antivirals, in addition to the LPV strategy, so her critical condition improved with 15 days of ECMO support. On the 23rd day, the endotracheal tube was successfully removed, and Ms. Chang stabilized and was discharged after 35 days of hospitalization.
Dr. How-Yang Tseng, who collaborated with the Information Technology Office to create the "ARDS real-time monitoring dashboard," added that Power BI consolidates all the medical data from different sources under the system and reflects them in the real-time monitoring dashboard to show the conditions and data trends of each patient. For example, doctors could monitor all the patients' condition through the unit distribution graph presenting with the ratio of ventilator, vasopressor, and continuous dialysis usage. According to the PF ratio, the related information would be ranked in a descending sequence to accelerate patient screening for identifying the target patients. Furthermore, it may help medical staff to quickly control the condition changes of patients so the LPV treatment strategy can be implemented earlier to elevate the cure rate.
CONTACT: Feng Ming Hsieh, a25050@mail.cmuh.org.tw